モデルを改善しようシリーズ② 時間をカテゴリ変数に
はじめに
当記事は、
のBaseCodeをどうにかして、
モデルを改善しようseriesです。
タイトルのように、
時間をカテゴリ変数にして行きます。
目次
背景
マーケットにおいて、価格の動く時間と動かない時間がある
というのはよく知られていることです。
これは、
「各主要国家のマーケットが開いている時間は、
活発に取引が行われるためレートが動きやすい。」
ということであると理解しています。
となると必然、時間帯によってボラティリティが変化します。
そして、取引する確率が増え、リターン予測が0(取引無し)に対する
改善が期待できるのではないかな、と考えました。
仮想通貨botterの方々は、既にもっと優れた方法で
時間帯によるボラティリティ問題に対応していると思いますが、
自分にはこれくらいしかおもいつきませんでした(泣)
特徴量を作っていこう
まずは設計を考えましょう。
設計
一口に「主要国家のマーケットが開いている」
といっても、依存する国家によって特徴がある気がしています。
主要マーケットは、
- 日本(東京)
- ヨーロッパ(ロンドン)
- アメリカ(ニューヨーク)
と言われております。
日本時間はボラティリティが少なく、
ロンドンで最も取引が行われ、
ニューヨークで荒れる、
みたいなイメージをしています。
日本時間はヨーロッパ、アメリカが夜ですのでボラティリティがないのは当たり前ですね。
話がそれましたが、
とにかく依存するマーケットによって相場に特色がある可能性があります。
ですので、マーケットが開いている、開いていない で分類するのではなく、
どこのマーケットが開いているか、
という分類をしていこうと思います。
もしくはシンプルに、「何時」というカテゴリで分類してしまってもいいかもしれません。
LightGBMなら、勝手に振り分けをしてくれちゃう気がします、、、
ということで、
hourで分類
こちらも行って、比較していこうと思います。
コード
df["open_market"] = df.index def datetime_to_hour(datetime_data): class TimeZoneException(Exception): pass if datetime_data.tzinfo is None: raise TimeZoneException("The timezone must be aware.") datetime_data = pd.Timestamp(datetime_data.astimezone(pytz.timezone("Europe/London"))) is_dst = False if datetime_data.dst().seconds>0: is_dst = True return is_dst def datetime_to_openmarket(datetime_data): """ If you put the datetime type in the argument, you can see which country's market is open. Returns ------- str which country's market is open """ dt_hour = datetime_data.hour is_dst = datetime_to_hour(datetime_data) if is_dst: if 8<=dt_hour and dt_hour<16: ret = "japan" elif 16<=dt_hour and dt_hour<17: ret = "japan_and_london" elif 17<=dt_hour and dt_hour<21: ret = "london" elif 21<=dt_hour and dt_hour<2: ret = "london_and_newyork" elif 2<=dt_hour and dt_hour<6: ret = "newyork" else: ret = "None" else: if 8<=dt_hour and dt_hour<17: ret = "japan" elif 17<=dt_hour and dt_hour<22: ret = "london" elif 22<=dt_hour and dt_hour<3: ret = "london_and_newyork" elif 3<=dt_hour and dt_hour<7: ret = "newyork" else: ret = "None" return ret #コメントアウトで選択できる #どの国のマーケットがあいているのか df["open_market"] = df["open_market"].map(datetime_to_openmarket) #hour(24時間) #change_tz_tokyo = lambda x: pd.Timestamp(x.astimezone(pytz.timezone("Asia/Tokyo"))) #df["open_market"] = df["open_market"].map(change_tz_tokyo) #df["open_market"] = df["open_market"].map(lambda x: x.hour) #one hot encoding df = pd.get_dummies(df, columns=["open_market"])
順番に見ていきます
df["open_market"] = df.index
まず、datetimeindexを持つDFのインデックスをカラムに保存します。
def datetime_to_hour(datetime_data): class TimeZoneException(Exception): pass if datetime_data.tzinfo is None: raise TimeZoneException("The timezone must be aware.") datetime_data = pd.Timestamp(datetime_data.astimezone(pytz.timezone("Europe/London"))) is_dst = False if datetime_data.dst().seconds>0: is_dst = True return is_dst
次にこちらの関数を用意します。
こちらの関数は、datetime型のデータを渡すと、 ロンドンをtimezoneに設定し、
ロンドンでサマータイムが時期かどうかを判定します。
tz_infoがnaiveな時、ロンドン時刻に変換できないので、
エラーを発生させるようにしてあります。
def datetime_to_openmarket(datetime_data): """ If you put the datetime type in the argument, you can see which country's market is open. Returns ------- str which country's market is open """ dt_hour = datetime_data.hour is_dst = datetime_to_hour(datetime_data) if is_dst: if 8<=dt_hour and dt_hour<16: ret = "japan" elif 16<=dt_hour and dt_hour<17: ret = "japan_and_london" elif 17<=dt_hour and dt_hour<21: ret = "london" elif 21<=dt_hour and dt_hour<2: ret = "london_and_newyork" elif 2<=dt_hour and dt_hour<6: ret = "newyork" else: ret = "None" else: if 8<=dt_hour and dt_hour<17: ret = "japan" elif 17<=dt_hour and dt_hour<22: ret = "london" elif 22<=dt_hour and dt_hour<3: ret = "london_and_newyork" elif 3<=dt_hour and dt_hour<7: ret = "newyork" else: ret = "None" return ret
こちらがメインの関数です。
ロンドンでのサマータイムを考慮して、
datetime型で与えられた時刻、どこのマーケットがオープンしているかを返します。
#コメントアウトで選択できる #どの国のマーケットがあいているのか df["open_market"] = df["open_market"].map(datetime_to_openmarket) #hour(24時間) #change_tz_tokyo = lambda x: pd.Timestamp(x.astimezone(pytz.timezone("Asia/Tokyo"))) #df["open_market"] = df["open_market"].map(change_tz_tokyo) #df["open_market"] = df["open_market"].map(lambda x: x.hour) #one hot encoding df = pd.get_dummies(df, columns=["open_market"])
こちらがメインのコードです。
先程定義した関数を利用して、["open_market"]カラムに、
どこのマーケットがオープンしているかを保存していきます。
現在時刻(hour)をカテゴリ変数にしたい場合は、
まずタイムゾーンを日本にします。
そして、何時かを["open_market"]カラムに保存します。
そして、pd.get_dummiesを使ってワンホットエンコーディングしていきます。
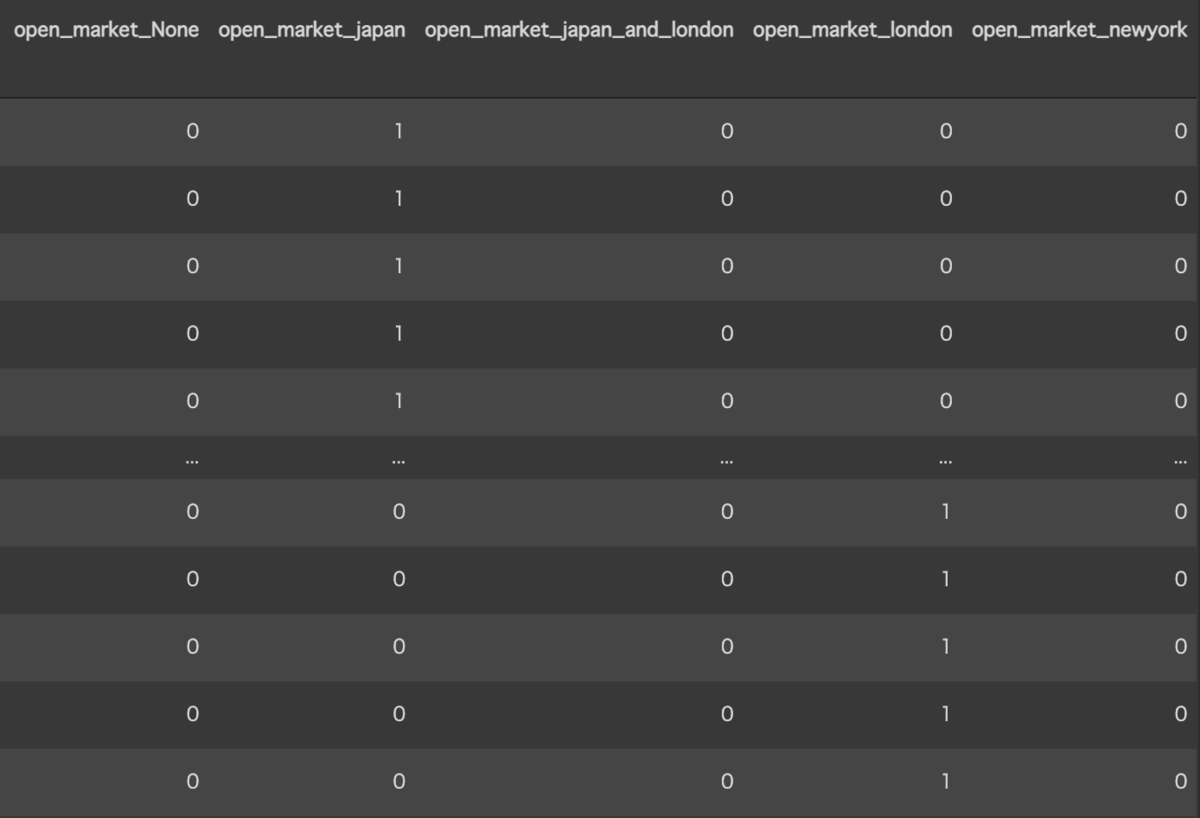
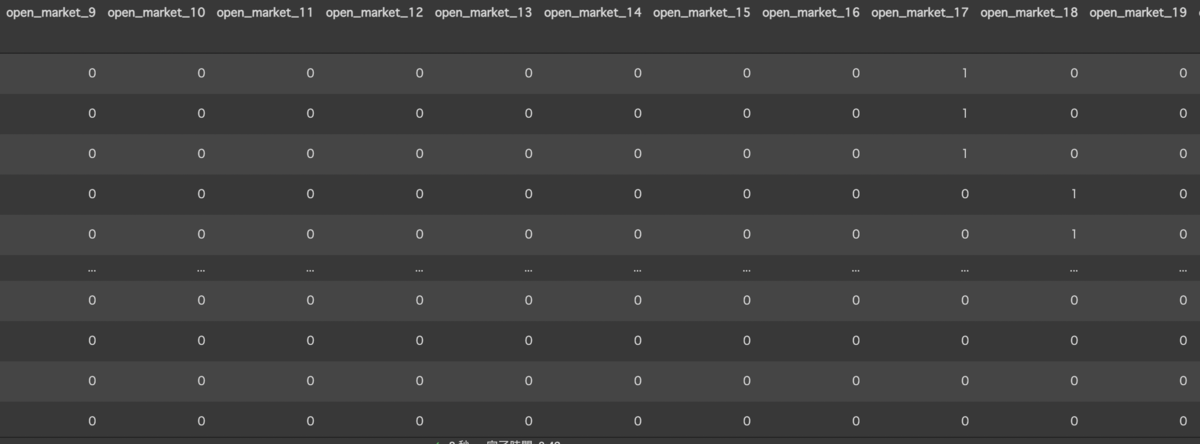
できたカラム
あいているマーケットで作成
時間(hour)で作成(一部)
時間を使った特徴量作成によるモデルへの影響
見づらいですが、
あいているマーケットで作成


時間(hour)で作成(一部)


考察
空いているマーケットで特徴量を作成した場合、
特徴量重要度において、ほとんど意味がないという結果になりました。
しかしながら、時間(hour)で特徴量を作成した場合、
それなりの重要度を持つことがわかりました。
特に売りの11時は顕著ですね。
時間を特徴量として組み込む場合、hourを入れてやることにします。